This article explains how to convert a flattened DataFrame to a nested structure, by nesting a case class within another case class.
You can use this technique to build a JSON file, that can then be sent to an external API.
Define nested schema
We’ll start with a flattened DataFrame.
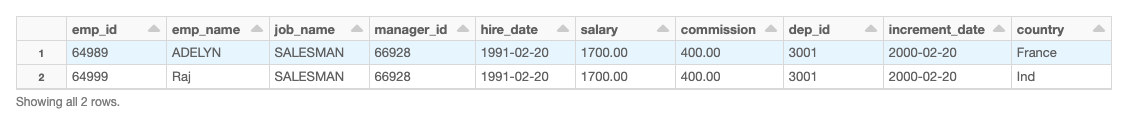
Using this example DataFrame, we define a custom nested schema using case classes.
%scala case class empId(id:String) case class depId(dep_id:String) case class details(id:empId,name:String,position:String,depId:depId) case class code(manager_id:String) case class reporting(reporting:Array[code]) case class hireDate(hire_date:String) case class emp_record(emp_details:details,incrementDate:String,commission:String,country:String,hireDate:hireDate,reports_to:reporting)
You can see that the case classes nest different data types within one another.
Convert flattened DataFrame to a nested structure
Use DF.map to pass every row object to the corresponding case class.
%scala
import spark.implicits._
val nestedDF= DF.map(r=>{
val empID_1= empId(r.getString(0))
val depId_1 = depId(r.getString(7))
val details_1=details(empID_1,r.getString(1),r.getString(2),depId_1)
val code_1=code(r.getString(3))
val reporting_1 = reporting(Array(code_1))
val hireDate_1 = hireDate(r.getString(4))
emp_record(details_1,r.getString(8),r.getString(6),r.getString(9),hireDate_1,reporting_1)
}
)This creates a nested DataFrame.
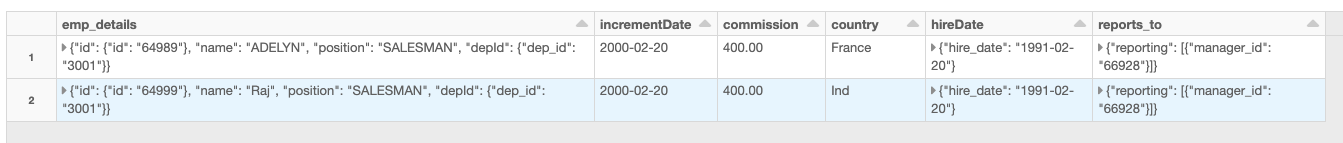
Write out nested DataFrame as a JSON file
Use the repartition().write.option function to write the nested DataFrame to a JSON file.
%scala
nestedDF.repartition(1).write.option("multiLine","true").json("dbfs:/tmp/test/json1/")Example notebook
Review the DataFrame to nested JSON example notebook to see each of these steps performed.